Menorrhagia Treatment in Goregaon West, Mumbai: Expert Solutions for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Dr. Dimple Doshi (MBBS, MD, DGO)
Lady Gynecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon
27+ years’ experience
20,000+ surgeries completed
- Are your periods unusually heavy, prolonged, or exhausting?
- Are you scheduling life around periods—work, travel, intimacy, even sleep?
- Do you soak pads every 1–2 hours, pass large clots, or feel severe cramps and pelvic pressure?
Why does menorrhagia feel so exhausting and scary?
Heavy bleeding can drain iron, energy, and confidence—while also creating fear about fibroids, polyps, or serious causes.
these may be your frequent statements:
- “I’m always tired, breathless, or dizzy.”
- “I feel embarrassed about staining and odor.”
- “I’m scared it could be fibroids or something dangerous.”
- “I want relief, but I want the right treatment—not random medicines.”
The best outcomes come from cause-based diagnosis, anemia correction, and stepwise treatment—medical first, minimally invasive when needed.
The good news? Menorrhagia is treatable.
With the right diagnosis, bleeding can be controlled while protecting the uterus and future fertility.
Find the cause → control bleeding → rebuild iron → treat the root problem → prevent recurrence.
At Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Dr. Dimple Doshi (MD, DGO) offers personalized, fertility-friendly treatment using medical therapy, hysteroscopic procedures, and advanced 3D laparoscopic surgery, planned according to your age, cause of bleeding, and reproductive goals.
Global & Indian Statistics:
- Up to 30% of women of reproductive age experience menorrhagia at some point in life.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding is a leading cause of iron-deficiency anemia in women worldwide (WHO).
- Structural causes like fibroids, adenomyosis, and endometrial polyps commonly contribute to chronic menorrhagia.
- Indian studies report that many women aged 30–45 years seek medical care for heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic and hysteroscopic treatments help reduce blood loss and recovery time while preserving fertility.
Sources: ACOG
Tired of heavy, exhausting periods? Get expert treatment options from Dr. Dimple Doshi.
What Is Menorrhagia (Heavy Periods)?
Menorrhagia means menstrual bleeding that is heavy or prolonged enough to affect daily life, cause anemia, or impact overall health.
You may be dealing with heavy menstrual bleeding if you experience:
- Bleeding lasting more than 7 days (ACOG)
- Soaking pads or tampons frequently or leaking through clothes or bedding (ACOG)
- Passing large clots, sudden “flooding,” or needing double protection
- Symptoms of anemia such as fatigue, breathlessness, dizziness, or palpitations
- Periods that interfere with work, travel, exercise, intimacy, or sleep
Synonyms of Menorrhagia
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB)
- Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)
- Excessive menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged periods
- Flooding periods
- Periods with clots
- Menstrual flooding
- Heavy bleeding per vaginum during periods
- Menometrorrhagia (heavy + irregular; often used informally)
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) (older term; now replaced by PALM–COEIN/AUB terminology)
What are the common causes of heavy menstrual bleeding?

Causes may be structural (fibroid/polyp/adenomyosis) or hormonal/medical—PALM-COEIN helps classify them.
I evaluate menorrhagia using the FIGO PALM–COEIN system (structured, practical, and internationally used). (PubMed)
Structural causes (PALM)
- P: Endometrial polyp
- A: Adenomyosis
- L: Leiomyoma (fibroids)
- M: Malignancy / hyperplasia (important to rule out in some age groups)
Non-structural causes (COEIN)
- C: Coagulopathy (esp. adolescents) (ACOG)
- O: Ovulatory dysfunction (PCOS, thyroid disorders, stress, perimenopause)
- E: Endometrial causes
- I: Iatrogenic (some medications like anticoagulantes/copper IUCD assosicated heavy flow)
- N: Not otherwise classified
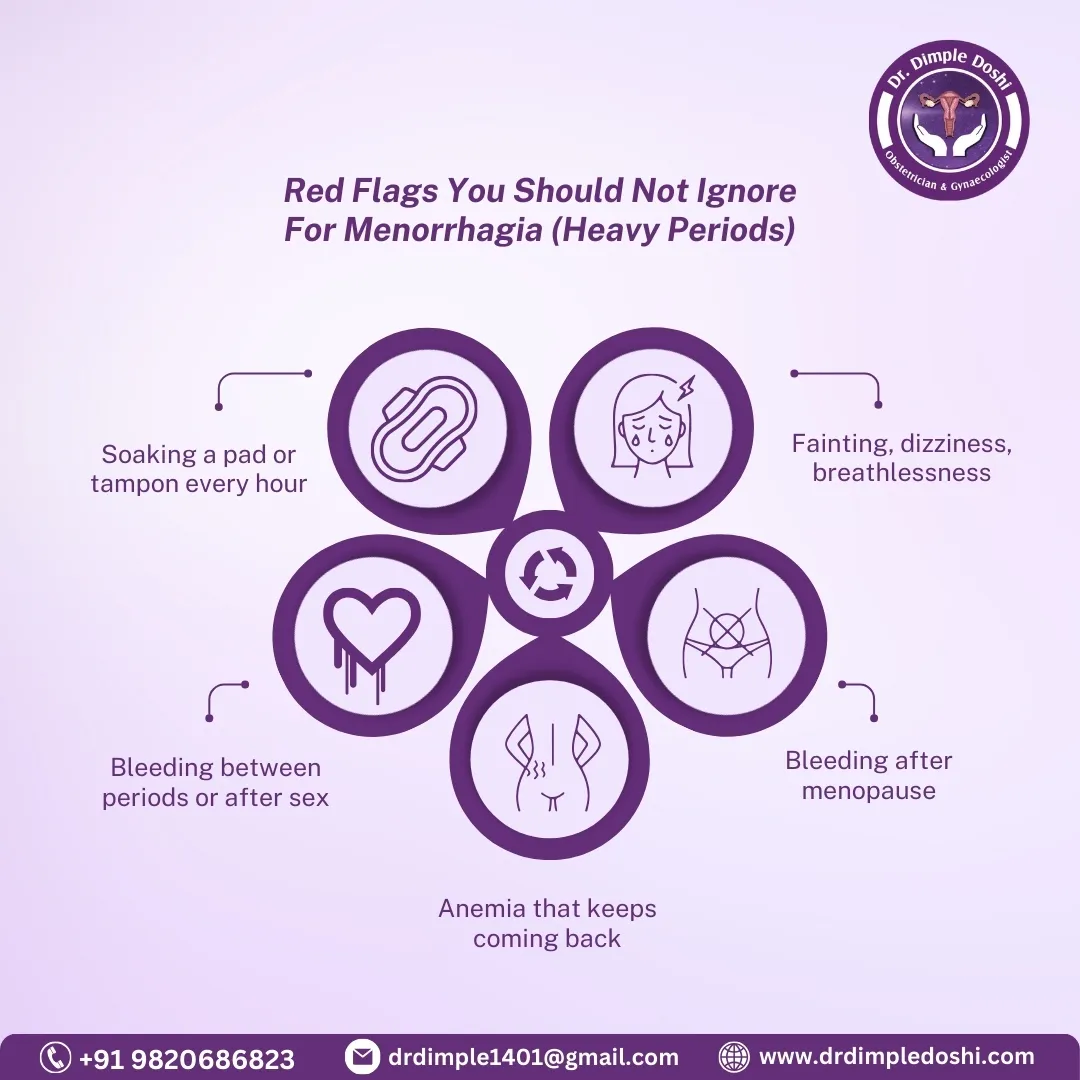
What symptoms and danger signs should you watch for?
Heavy bleeding is treatable, but sudden very heavy bleeding, fainting, or bleeding after menopause needs urgent evaluation.

Common symptoms
- Heavy flow, clots, “flooding”
- Prolonged bleeding (>7 days) (ACOG)
- Pelvic pain/pressure (often with fibroids/adenomyosis)
- Weakness, fatigue, low stamina (often anemia)
Red flags (don’t ignore)
- Soaking 1 pad/tampon every hour for several hours
- Fainting, severe dizziness, breathlessness
- Bleeding after sex or between periods repeatedly
- Bleeding after menopause
- Known anemia that keeps returning
How is menorrhagia diagnosed?
Diagnosis is history + exam, then pregnancy test (if relevant), anemia work-up, ultrasound, and targeted tests like biopsy or hysteroscopy.
What I focus on in your consultation
- Pattern: duration, flooding, clots, pain, intermenstrual bleeding
- Anemia symptoms and quality-of-life impact
- Contraception, medicines, fertility goals
- Exam (only when appropriate and comfortable)
Common investigations
- Pregnancy test (when applicable)
- CBC (Hb, indices) + serum ferritin
- Iron studies (Ferritin)
- TSH
- Pelvic ultrasound (often transvaginal if suitable)
- Pap smear if due
When additional tests help
- Hysteroscopy: see + treat polyps/submucous fibroids
- Endometrial biopsy: based on age/risk factors/pattern
- Coagulation profile: selected adolescents/strong history
- SIS (saline sonography): better for cavity lesions
What is the step-by-step patient journey at Vardaan Hospital?
Your pathway is structured: evaluate → correct anemia → choose the least invasive effective option → follow-up to prevent recurrence.
- Consult + evaluation
- CBC/ferritin/TSH + ultrasound
- Start bleeding control + iron plan
- Decide: medical / LNG-IUS / hysteroscopy / laparoscopy
- Procedure if needed (often daycare/short-stay)
- Follow-up: symptom check + Hb/ferritin correction + recurrence prevention
What are the Non Surgical treatment options for menorrhagia?
Treatment is individualized—iron correction + bleeding control first, then cause-based options like LNG-IUS, hysteroscopy, or laparoscopy.
What are the treatment goals?
- Stop bleeding safely
- Correct anemia and rebuild ferritin
- Treat the root cause
- Protect fertility if desired
- Reduce recurrence
Which non-surgical treatments can reduce bleeding?
Many women improve with medicines and iron therapy—especially when a large fibroid/polyp isn’t the main cause.
Common options (case-based):
- Iron therapy (oral or IV) + ferritin correction
- Tranexamic acid during menses (if suitable)
- NSAIDs (also help period pain)
- Hormonal therapy (chosen based on profile)
- LNG-IUS (Levonorgestrel intrauterine system) for strong bleeding reduction in many women
- Blood Transfusion may be needed in severe cases with extremely low hemoglobin levels
When do you need surgery for heavy menstrual bleeding?
Surgery is considered when medicines fail, a structural cause is present, anemia is severe, or quality of life is significantly affected.
You may be a surgical candidate if:
- Bleeding persists despite adequate medical therapy
- Ultrasound shows fibroids/polyps/adenomyosis causing symptoms
- You have recurrent anemia or transfusion-level blood loss
- You want a definitive solution (especially after family completion)
Which procedures are commonly done?
- Hysteroscopy (diagnosis + treatment of polyps/submucous fibroids)
- D and C and endometrial sampling
- Myomectomy (fibroid removal):
– Laparoscopic myomectomy
– Hysteroscopic myomectomy
– Open myomectomy - Laparoscopic surgery for adenomyosis/endometriosis (selected cases)
- Hysterectomy (definitive option in carefully chosen patients)
How does 3D laparoscopy help at Vardaan Hospital?
With the Karl Storz Rubina 3D laparoscopic system, depth perception and precision improve—helping in:
- safer dissection around bladder/ureter/bowel
- better suturing, hemostasis, and tissue handling
- smaller cuts and typically faster recovery (when compared with open surgery)
How can you prevent heavy periods and anemia?
You can’t prevent every cause, but early evaluation, anemia correction, hormonal balance, and timely treatment prevent worsening and recurrence.
Why is early gynecological evaluation important?
Early detection of fibroids, polyps, adenomyosis, thyroid disorders, or endometrial changes prevents progression to severe bleeding.
When should prevention shift to treatment?
If bleeding lasts >7 days, clots are frequent, cycles affect daily life, or anemia develops, active treatment is needed rather than observation.
Does correcting anemia prevent worsening of menorrhagia?
Absolutely. Treating iron deficiency early prevents fatigue, hair fall, and further cycle disturbances that can worsen bleeding.
Can medicines help in prevention?
Yes. When advised, hormonal tablets, progesterone therapy, or LNG-IUS can effectively control and prevent recurrent heavy bleeding.
Can hormonal imbalance be prevented?
Maintaining healthy weight, avoiding crash diets, and timely medical guidance help keep estrogen–progesterone balance stable.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent heavy periods?
Yes. Balanced nutrition, iron-rich foods, regular exercise, stress control, and adequate sleep support hormonal balance and reduce bleeding risk.
Who is the best doctor for menorrhagia treatment in Goregaon West, Mumbai?
The best doctor for menorrhagia treatment is one who offers cause-based diagnosis, fertility-sensitive care, and minimally invasive treatment options—not one-size-fits-all solutions.
Dr. Dimple Doshi is widely trusted for managing menorrhagia because she focuses on:
Identifying the exact cause of heavy bleeding
Preserving the uterus and fertility whenever possible
Using medical, hysteroscopic, and advanced laparoscopic techniques
Explaining options clearly and recommending surgery only when necessary
Why Dr. Dimple Doshi
- 25+ years experience
- 25,000+ surgeries
- Clear, calm explanations and stepwise decision-making
- Strong focus on minimally invasive gynecology
Why Vardaan Hospital (Goregaon West, Mumbai)
- Women-centric setup and safety-first protocols
- Daycare hysteroscopy + advanced laparoscopy facilities
- Karl Storz Rubina 4K 3D system available for selected cases
Medical Code for Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia / AUB codes (ICD-10)
- N92.0 – Excessive and frequent menstruation with regular cycle (classic “menorrhagia”)
- N92.1 – Excessive and frequent menstruation with irregular cycle (often overlaps with “menometrorrhagia”)
- N92.2 – Excessive menstruation at puberty
- N92.4 – Excessive bleeding in the premenopausal period
- N92.6 – Irregular menstruation, unspecified
- N93.8 – Other specified abnormal uterine and vaginal bleeding
- N93.9 – Abnormal uterine and vaginal bleeding, unspecified
Common cause codes (ICD-10)
- D25.0 – Submucous leiomyoma of uterus
- D25.1 – Intramural leiomyoma of uterus
- D25.2 – Subserosal leiomyoma of uterus
- D25.9 – Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified
- N84.0 – Polyp of corpus uteri (endometrial polyp)
- N80.0 – Endometriosis of uterus (commonly used for adenomyosis)
- N85.0 – Endometrial glandular hyperplasia
- E28.2 – Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) (when relevant)
- E03.9 – Hypothyroidism, unspecified (when relevant)
Anemia codes commonly used (ICD-10)
- D50.0 – Iron deficiency anemia secondary to blood loss (chronic)
- D50.9 – Iron deficiency anemia, unspecified
Coding note: The “best” ICD code depends on what you document—cycle regularity, duration, age group, and confirmed cause (fibroid/polyp/adenomyosis)
FAQs – Heavy Periods and Menorrhagia Management
Q1. How long does menorrhagia usually last?
Ans. Menorrhagia typically lasts longer than 7 days, which is considered abnormal for menstrual bleeding.
Q2. How much blood loss is considered heavy during a period?
Ans. Losing more than 80 ml of blood per cycle or soaking through a pad/tampon every 1–2 hours is considered heavy bleeding.
Q3. What are the common complications of untreated menorrhagia?
Ans. Untreated menorrhagia can lead to severe anemia, fatigue, dizziness, and in rare cases, heart complications.
Q4. Can menorrhagia affect fertility?
Ans. Yes, chronic heavy periods may indicate underlying conditions like PCOS or fibroids, which can impact fertility.
Q5. What foods should you avoid during heavy periods?
Ans. Avoid high-salt, processed foods, and caffeine as they can worsen bloating and discomfort during heavy periods.
Q6. Can stress cause menorrhagia?
Ans. While stress doesn’t directly cause menorrhagia, it can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially leading to irregular or heavy bleeding.
Q7. Is menorrhagia linked to PCOS?
Ans. Yes, PCOS can cause irregular cycles and heavy bleeding, but menorrhagia can also occur without PCOS.
Q8. Can you get pregnant if you have menorrhagia?
Ans. Yes, pregnancy is possible, but it may be challenging if the heavy bleeding is due to hormonal imbalance or other underlying issues.
Q9. What is the first-line treatment for menorrhagia?
Ans. The first line of treatment includes medications like NSAIDs, tranexamic acid, or hormonal therapy, depending on the cause.
Q10. When should you go to the hospital for heavy periods?
Ans. If you are soaking a pad every hour for several hours or feel dizzy, weak, or short of breath, seek emergency care immediately.
Q11. What vitamin deficiencies can worsen heavy bleeding?
Ans. Iron and Vitamin K deficiencies can contribute to prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding.
Q12. Can heavy periods be controlled without surgery?
Ans. Yes, most cases of menorrhagia are managed with medication, hormonal therapy, and lifestyle changes before considering surgery.
Q13. What is the role of diet in managing menorrhagia?
Ans. A diet rich in iron, Vitamin C, and folate helps replenish lost nutrients and reduce anemia caused by heavy periods.
Q14. How do doctors diagnose the cause of heavy bleeding?
Ans. Diagnosis may involve blood tests, ultrasound, hysteroscopy, or endometrial biopsy to identify underlying causes.
Q15. Can hormonal birth control help with menorrhagia?
Ans. Yes, birth control pills or hormonal IUDs are often prescribed to regulate menstrual flow and reduce heavy bleeding.
Still have questions about heavy bleeding, periods, or anemia? Get clarity from Dr. Dimple Doshi’s expert team.
Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.