Uterine and Cervical Polyps: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Many women come to me worried about irregular bleeding, spotting, or discharge, only to discover that the cause is something quite common—uterine or cervical polyps. These growths are usually benign, but they can interfere with comfort, fertility, and peace of mind. The good news is that with early diagnosis and the right treatment, polyps are easily manageable.
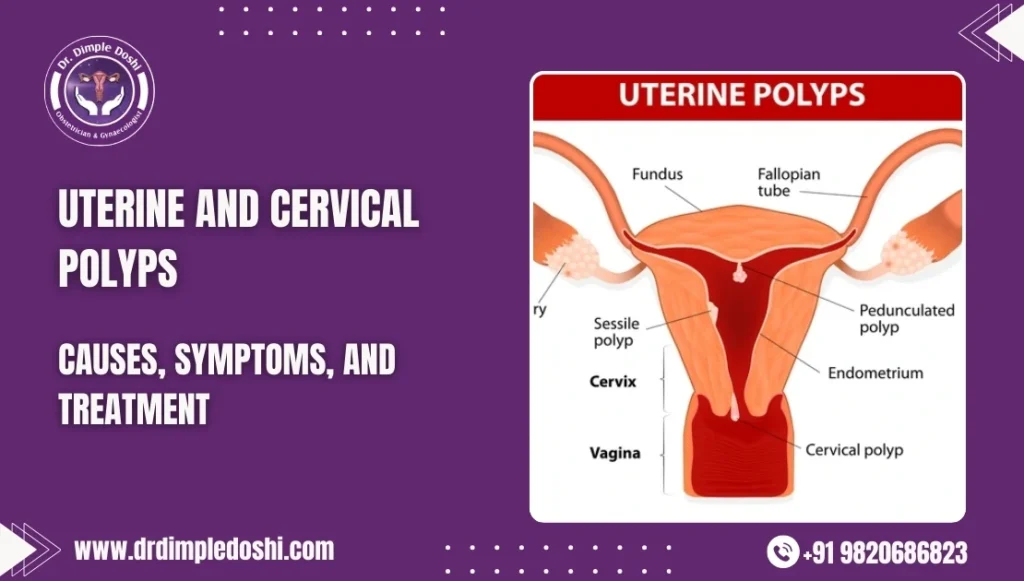
What are uterine and cervical polyps?
Uterine and cervical polyps are overgrowths of the uterine lining or cervical tissue. They are soft, spongy, and sometimes firm, and may appear cherry-red, reddish-purple, or greyish-white in colour.
- Uterine polyps grow inside the uterus, where pregnancy develops
- Cervical polyps grow from the cervix, and may sometimes be visible outside the vagina
In my clinical experience, most women are surprised to learn how common polyps actually are.
What are the different types of uterine and cervical polyps?
Endometrial (uterine) polyps
- Develop inside the uterine cavity
- Can be single or multiple
- May affect menstrual flow and fertility
Cervical polyps
These arise from the cervix and are of two types:
- Endocervical polyps: Grow from inside the cervical canal
- Ectocervical polyps: Grow on the outer surface of the cervix and may be visible on examination
What causes uterine and cervical polyps?
Polyps develop due to hormonal imbalance and local tissue overgrowth. Common contributing factors include:
- Abnormal response to estrogen
- Chronic infection or inflammation of the uterus or cervix
- Obesity and excess body fat (increases estrogen levels)
- High blood pressure
- Increasing age and menopause
- PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease)
- Use of medications like tamoxifen for breast cancer
Dr. Dimple Doshi’s Tip:
Anything that increases long-term estrogen exposure can increase the risk of polyp formation.
What symptoms do uterine or cervical polyps cause?
Many polyps—especially small ones—may cause no symptoms at all. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged spotting
- Bleeding between periods
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Persistent vaginal discharge or recurrent infections
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse
Any abnormal bleeding, especially after menopause, must always be evaluated.
How are uterine and cervical polyps diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of examination and imaging:
Gynecological examination:
Can detect visible cervical polypsUltrasonography:
Helps identify polyps inside the uterusHysteroscopy:
Direct visualization of the uterine cavity; the most accurate methodBiopsy or D&C:
Polyps may sometimes be detected incidentally during tissue sampling
In my practice, hysteroscopy provides the clearest diagnosis with the least discomfort.
How are uterine and cervical polyps treated?
Treatment depends on size, symptoms, age, and reproductive plans.
Observation
- Small, symptom-free polyps may be monitored with regular ultrasounds
OPD removal
- Visible ectocervical polyps can often be removed safely in the clinic without anesthesia
Hysteroscopic polypectomy
- Gold standard treatment
- Minimally invasive
- Complete removal under direct magnified vision
- Best option for uterine polyps
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
- A blind procedure that removes the uterine lining along with the polyp
- Less precise than hysteroscopy
Medications
- Limited role
- Progesterone tablets or GnRH agonists may temporarily shrink small polyps by counteracting estrogen
Dr. Dimple Doshi’s Tip:
Complete removal is important—partial treatment increases the risk of recurrence.
Can uterine polyps be prevented?
While polyps cannot always be prevented, certain steps reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Control blood pressure and metabolic health
- Manage PCOD effectively
- Attend regular gynecological check-ups
- Treat vaginal and cervical infections promptly
- Practice safe sexual habits
Conclusion
Uterine and cervical polyps are common, usually benign, and highly treatable conditions. Early detection through routine gynecological check-ups and timely treatment prevents complications such as heavy bleeding, infection, infertility, and anxiety.
At Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai, I emphasize early diagnosis, minimally invasive treatment, and personalized care. If you notice abnormal bleeding or persistent discharge, do not ignore it—your body is asking for attention, and timely care makes all the difference.
